Vocal Cord Nodule
How does a vocal cord nodule occur?
A vocal cord nodule is a name given to benign (i.e. not associated with vocal cord cancer) growths that form on the free surface where the vocal cords come into contact. They develop due to misuse or overuse of the voice. Since they are caused by long-term use of the voice at the wrong volume, wrong pitch or inappropriate strain, they can be roughly similar to calluses on our hands or feet.
Who are the most common people with vocal cord nodules?
Teachers, voice artists, news announcers, call centre workers and religious officials are among the people who use their voices professionally and are much more common than other segments of society. It is one of the leading causes of hoarseness.
Are Vocal Cord Nodules Seen in Children?
Vocal cord nodules can also be seen in childhood. The most common cause of long-term hoarseness in childhood is vocal cord nodules. In children, vocal cord nodules are more frequently seen in boys than in girls. Just like adults, the most common cause is excessive or incorrect use of the voice. Additionally, children who frequently experience upper respiratory infections, clear their throat often, have allergies and throat reflux, study in crowded classrooms, or have multiple siblings also tend to develop vocal cord nodules more frequently.
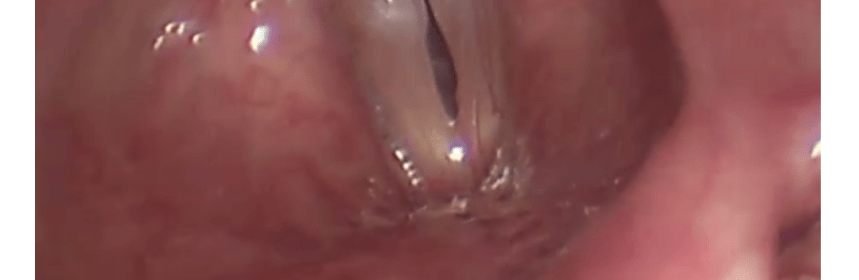
Are Vocal Cord Nodules More Common in Women?
Though vocal cord nodules can be seen in individuals of all ages and genders, they are seen much more frequently in adult women than in men. Before puberty, on the contrary, they are seen more in boys than in girls.
What Are the Symptoms of Vocal Cord Nodules?
The symptoms of vocal cord nodules are generally hoarseness, change in voice, breathy voice, and roughness in voice. A professional voice user may express that their voice has come out at a lower pitch or that their voice is more breathy, raspy, and grating than normal. Professional voice users may notice a narrowing in their vocal range.
In addition to changes in their voice, individuals may complain of pain in the neck muscles due to increased voice use, as well as difficulty speaking and even swallowing.
How Do Vocal Cords Work?
The vocal cords are composed of two structures, which are connected at one end and spread apart at the other, resembling the letter V. These structures contain muscles inside and the soft tissue known as mucosa on the outside.
During speech, the vocal cords of an average man strike each other about 120 times per second, while a woman's vocal cords strike about 200 times. Therefore, the vocal cords are the soft tissue in the body most susceptible to trauma.
When Should One See a Doctor About Vocal Cord Nodules?
Individuals who do not use their voices professionally should see a voice doctor if hoarseness lasts more than 2 weeks. A professional voice user generally does not have the luxury of waiting this long. Your voice doctor will want to listen to your complaints and ensure they have adequate information about your voice health and overall medical history before learning about your professional vocal expectations in detail. Itâs important to note that a person needing diagnosis and treatment for their professional voice does not necessarily have to be a vocal artist. In fact, many professions require individuals to express themselves and their work vocally throughout the day. These include teachers, lawyers, call center employees, bank, municipal, postal service workers who need their voices for customer service, shopkeepers, tradespeople, religious officials, and many other professions.
How are the vocal cords examined? How is a vocal cord nodule diagnosed?
The diagnosis and determination of the cause of vocal cord nodules can be made by a detailed examination of your voice and vocal cords (the ideal combination in this regard is laryngovideostroboscopy and objective voice analysis).
Which factors play a role in the formation of vocal cord nodules?
The primary factor in the formation of vocal cord nodules is misuse or overuse of the voice. In addition, other causes can also contribute to the formation of vocal cord nodules. These include laryngopharyngeal reflux, allergies, psychological factors, and personality traits. In fact, the last two factors also influence the formation of vocal cord nodules because they can lead to overuse or misuse of the voice. Individuals with vocal cord nodules are often observed to be more extroverted, participate in social activities more often, and are aggressive and motivated.
How are vocal cord nodules treated? What are the Options?
There are two basic methods in the treatment of nodules: Voice therapy and vocal cord surgery.
The ideal way to treat a nodule caused by misuse or overuse of the voice is to stop using the voice in that way. Developing habits of using the voice correctly and using proper vocal techniques to avoid excessive pressure on the vocal cords will not only make the nodules smaller or even disappear, but also eliminate the risk of recurrence. The primary method of teaching correct voice use is voice therapy.
Voice therapy is usually sufficient as a stand-alone treatment for most nodules. Voice therapy is a form of treatment that should be tailored to the clinical situation and needs of each individual. The framework of the voice therapy plan is drawn according to the patient's age, level of voice use and whether he or she has any professional aspirations for his or her voice. There are some main issues that should be included in every therapy programme. These include informing the patient about the behaviours that cause or worsen nodule formation, minimising these behaviours and implementing new behavioural and environmental changes appropriate for voice use and professionalism.
However, some nodules are resistant to treatment, including voice therapy. Vocal cord nodules that do not heal despite strict adherence to proper vocal hygiene rules and correct vocal techniques are treated with special surgery called phonemic surgery, which is performed under general anaesthesia with the aid of a microscope.





